Get in touch!
We're here to help - feel free to reach out with any questions, thoughts, or requests, and we’ll get back to you as soon as we can.
We're here to help - feel free to reach out with any questions, thoughts, or requests, and we’ll get back to you as soon as we can.
Sign up for our newsletter to receive exclusive discounts and promotions.

In a world where sleep struggles are all too common, melatonin has emerged as a trusted natural remedy. This powerful hormone not only regulates our sleep-wake cycle but also offers a range of other health benefits. Whether you’re dealing with occasional sleeplessness, jet lag, or simply looking to enhance your overall well-being, melatonin supplementation might be the solution you need. But how does melatonin work, and what makes it so effective? Let’s explore the science behind this fascinating compound.
Melatonin is a hormone naturally produced by the pineal gland in response to darkness. It helps regulate the body’s circadian rhythm, signalling when it’s time to sleep and wake up. However, factors such as excessive screen time, shift work, ageing, and stress can disrupt melatonin production, leading to sleep difficulties. Supplementing with melatonin can help restore balance and improve overall sleep quality [1].
Melatonin is best known for its ability to promote restful sleep. Scientific research highlights several key benefits:
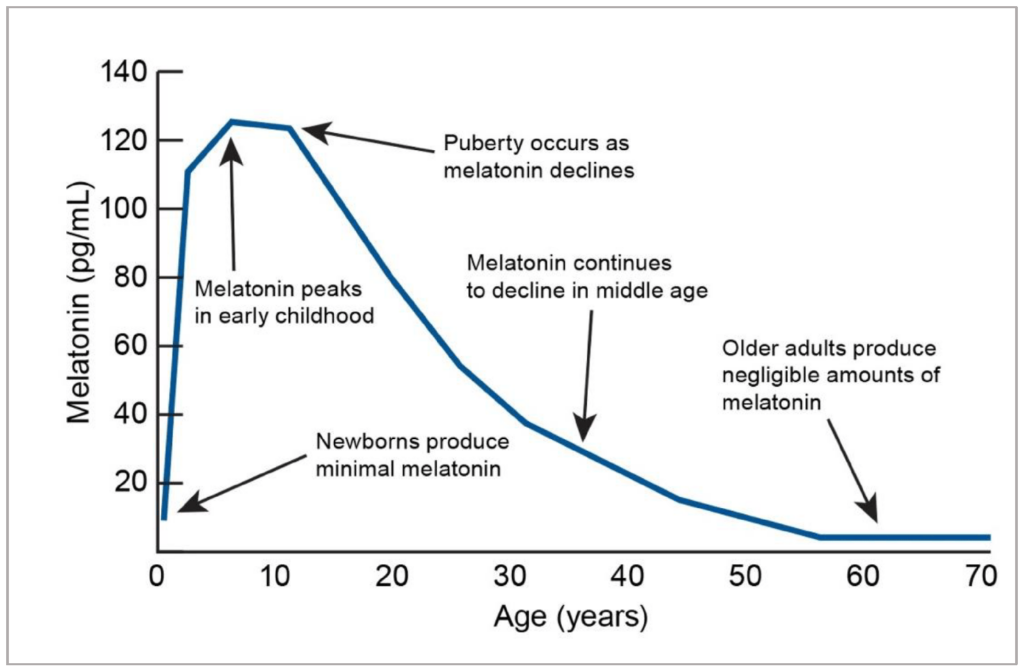
The most well-known benefit of melatonin is its ability to promote better sleep. Melatonin helps regulate your body’s internal clock, signalling to your brain that it’s time to sleep. For individuals with insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns, such as shift workers or those experiencing jet lag, melatonin supplementation can be particularly effective. Studies have shown that melatonin can reduce the time it takes to fall asleep, increase total sleep duration, and improve sleep quality [6].
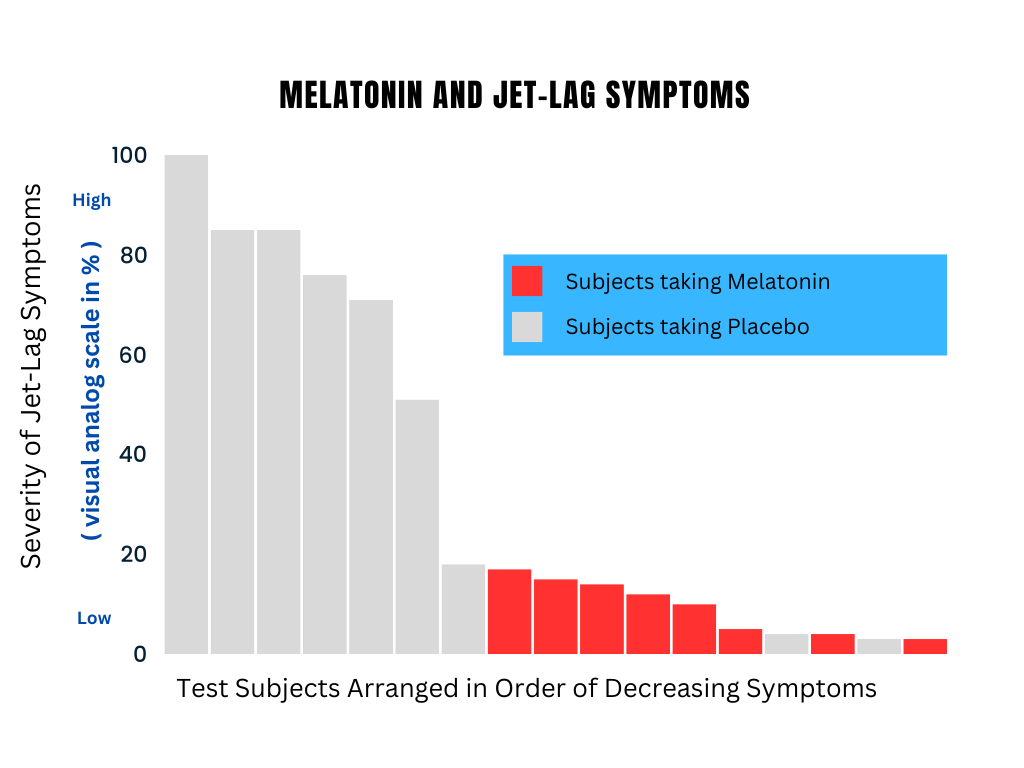
Jet lag occurs when your internal clock is out of sync with the time zone you’re in, often resulting in sleep disturbances, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. Melatonin can help realign your circadian rhythm with the new time zone, reducing the symptoms of jet lag. Taking melatonin at the appropriate time before your flight and during your trip can make the transition smoother and help you adapt more quickly to the new time zone.
While melatonin is primarily associated with sleep, emerging research suggests it has several other important health benefits:
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that occurs at certain times of the year, usually in the winter when daylight hours are shorter. Melatonin levels can be affected by the reduced exposure to natural light, contributing to the symptoms of SAD. Supplementing with melatonin can help regulate these levels and improve mood, making it a useful tool in managing SAD [11].
Melatonin is a powerful antioxidant, which means it helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to ageing and diseases such as cancer. Melatonin’s antioxidant properties can help neutralise these harmful molecules, reducing oxidative stress and potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases [12].
Research suggests that melatonin can also support the immune system. It helps regulate immune responses and has been shown to enhance the activity of various immune cells, including T cells and natural killer cells. This immune-boosting effect can help your body better defend itself against infections and diseases [13].
Melatonin may play a role in protecting eye health. It has been found to have protective effects against conditions like age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and glaucoma. Its antioxidant properties help reduce oxidative damage in the eyes, which can contribute to these conditions [14].
To maximise the benefits of melatonin, it’s essential to use it correctly. Here are some guidelines for safe and effective supplementation:
Melatonin is more than just a sleep aid—it’s a powerful hormone with broad-ranging benefits for overall health. Whether you’re looking to improve sleep quality, support immune function, or protect against oxidative stress, melatonin can be an invaluable addition to your wellness routine. By using it wisely and in alignment with your body’s needs, you can unlock its full potential for better sleep and beyond.